Spice AI
Overview
Spice.ai is an open-source data and AI platform offering zero-ETL SQL federation, acceleration, and hybrid search for data-intensive applications and AI agents.
Spice extends Supabase’s scalable Postgres foundation by federating data lakes, warehouses, and APIs, accelerating queries, and enabling hybrid search across structured and unstructured data. Together, Spice and Supabase deliver a complete open-source stack for building AI-native apps that are grounded in up-to-date enterprise context without complex pipelines.
By connecting Supabase to Spice, developers can:
- Query Supabase alongside any other data sources (S3, MySQL, Postgres, Snowflake, Databricks, Oracle, Kafka, etc.) in a single SQL statement
- Accelerate Supabase tables locally for sub-second queries - materialize frequently accessed datasets for more responsive dashboards, APIs, and applications.
- Add hybrid search (vector and full text search) to Supabase tables without modifying schemas
- Call AI models (OpenAI, Anthropic, local models) directly from SQL using Supabase data
- Provision secure AI sandboxes that expose only the minimal, policy-filtered Supabase data required for each agent or model
- Use MCP to access all connected data sources and tools in a single endpoint.
Why use Spice with Supabase?
Accelerate your Supabase queries
Run complex or high-volume SQL queries in milliseconds across multiple backend data sources by caching and indexing working sets in the Spice runtime. This is ideal for analytics, dashboards, internal tools, and performance-sensitive APIs.
Federate Supabase with all your data
Join Supabase tables with data stored in object storage, warehouses, or other operational databases.
Add hybrid search to Supabase
Automatically vectorize and full-text index data sources and query them using SQL. No additional search service or embedding infrastructure required.
Integrate AI with Supabase and third party data
Call OpenAI, Anthropic, or local LLMs from SQL, OpenAI-compatible APIs, and MCP and ground them in Supabase tables.
Secure AI sandboxing for Supabase data
Protect your Supabase and production data by provisioning temporary, scoped AI sandboxes in Spice and ensure AI agents or models receive only the minimum data required, governed by detailed policies with full observability.
Eliminate ETL and pipelines
Spice queries Supabase where in place and accelerates data alongside your compute, preserving Supabase as the source of truth while reducing operational complexity.
Features
Unified SQL
Query Supabase alongside any other system using a single SQL interface.
Local acceleration
Materialize Supabase tables in the Spice runtime for significantly faster queries and faster application response times.
Hybrid SQL search
Add embeddings and full-text indexes to any Supabase table and query them together using SQL.
Deployment optionality
Run Supabase and Spice.ai Open Source locally, at the edge, or on the fully managed Spice.ai Cloud Platform. Lightweight, portable, and designed for scale.
Use cases for Supabase developers
- Data-intensive applications that query across Supabase, S3, and analytics systems
- Hybrid vector and full-text search across structured and unstructured data
- AI-powered applications that need fast access to Supabase tables
- Real-time APIs backed by Supabase data
- Internal tools with sub-second query performance
- Operational analytics with zero ETL
How to connect Spice to Supabase
Follow these steps to get started with Supabase using the PostgreSQL Data Connector.
Pre-requisites
- Supabase project.
- Spice is installed (see the Getting Started documentation).
Steps
Step 1. From a Supabase project select Project Settings from the sidebar navigation.
Step 2. Navigate to Database under Configuration.
Step 3. Find the Connection parameters section.
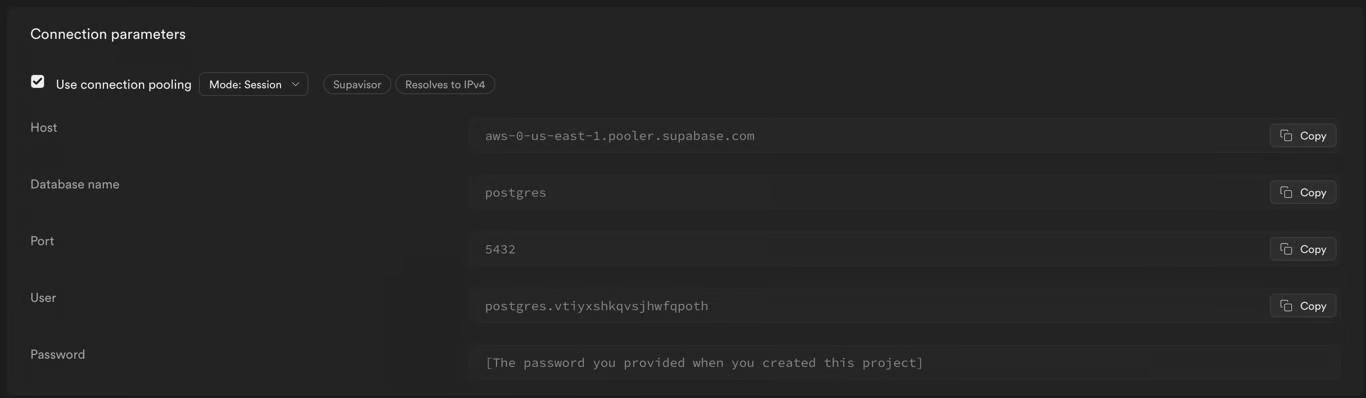
Step 4. Edit the spicepod.yaml file in this directory and replace [remote_table_path] with the path to the Supabase table to be accelerated, [local_table_name] with your desired name for the locally accelerated table, and the params section with the connection parameters from the Supabase project.
See the datasets reference for more dataset configuration options and PostgreSQL Data Connector for more options on configuring a PostgreSQL Data Connector.
Ensure the PG_PASS environment variable is set to the password for your Supabase instance. Environment variables can be specified on the command line when running the Spice runtime, or in a .env file in the same directory as spicepod.yaml.
_10echo "PG_PASS=<password>" > .env
To securely store the Supabase password, see Secret Stores
Step 5. Run the Spice runtime with spice run from this directory.
Follow the Spice getting started guide to get started with the Spice runtime.
Step 6. Run spice sql in a new terminal to start an interactive SQL query session against the Spice runtime.
For more information on using spice sql, see the CLI reference.
Step 7. Execute the query select * from [local_table_name]; to see the Supabase table accelerated locally.
Details
Third-party integrations and docs are managed by Supabase partners.



